Usually, the focus is on how the Russian Federation mobilizes on its territory for the war against Ukraine, while the mobilization of residents of the temporarily occupied territories of our country to the enemy army remains an issue that is both acute and unsolved.
Against this background, an overview of Polish Defence24 website, dedicated to the formation of infantry units for the Russian occupation forces, which, in particular, reveals the issue of mobilization in the temporarily occupied Donbas to the “1st and 2nd Army Corps”, which now function as the 3rd and 51st Armies as part of the Russian Armed Forces.
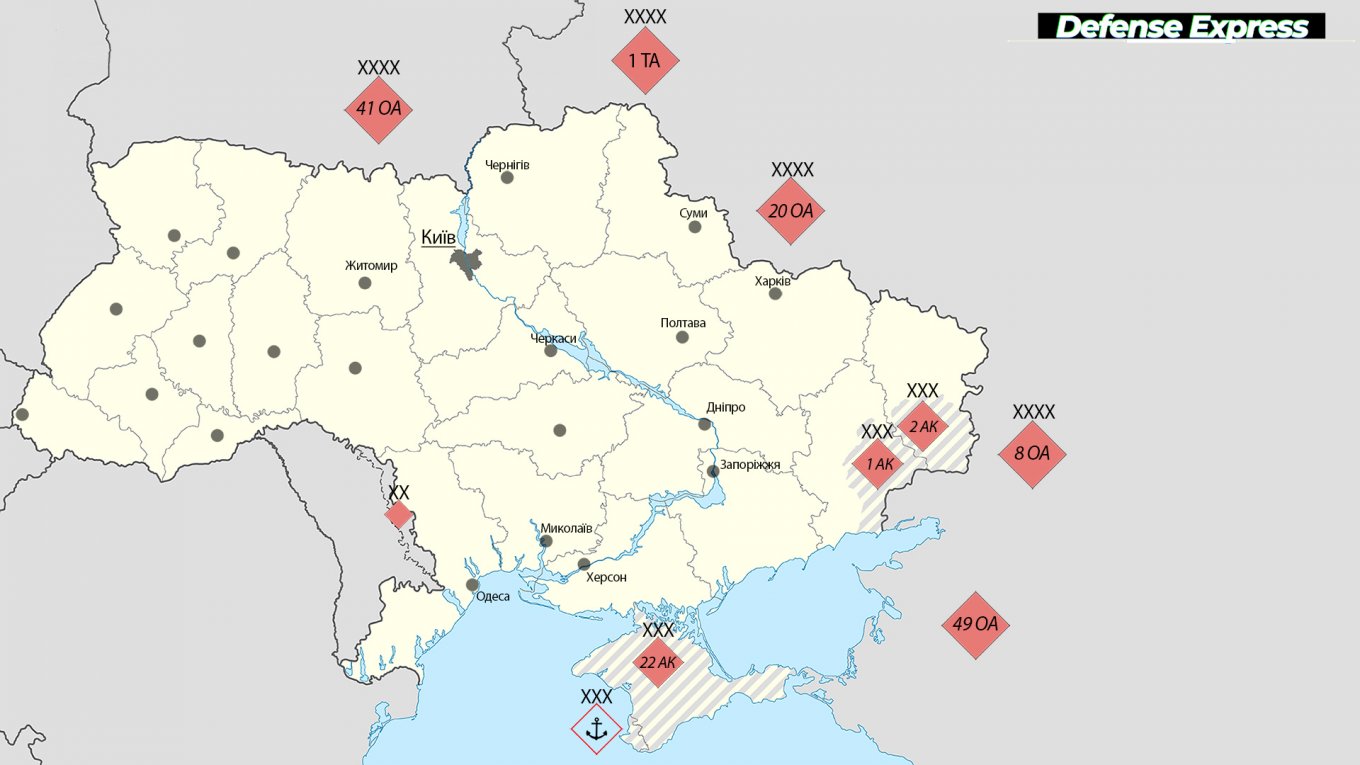
The picture presented in this review looks like this. The Russian occupiers began to carry out forced and illegal mobilization to wage a full-scale war against Ukraine back in February 2022.
As part of such mobilization, the ruscists for the “1st Army Corps” in the TOT of the Donetsk region created as many as 17 “mobilization” infantry regiments, which were originally numbered from 101 to 133. In turn, for the “2nd Army Corps” in the TOT of the Luhansk region, the occupiers created four “mobilization” infantry regiments, which were numbered from the 202nd to the 208th number.
The status of an infantry regiment meant that such a unit did not have its own heavy weapons and equipment, the main bet was on the use of “live mass”. The total number of losses of such “mobilization” infantry regiments of the Russian occupiers in Donbas remains unknown.

At the same time, it should be emphasized that the above-mentioned “mobilization” infantry regiments at the time of their formation (i.e. at the beginning of 2022) were not considered by the Kremlin itself to be an “official part” of its armed forces, although in fact the “1st and 2nd Army Corps” were directly subordinate to the command of the 8th Army of the Southern Military District of the Russian Armed Forces.
At the end of 2022, the ruscists began the “official” integration of the “1st and 2nd Army Corps” into their armed forces. As part of this, infantry battalions were created in the structure of both “AKs” with the status of “separate” and serial numbers from the 266th number for the “1st AK” and from the 291st for the “2nd AK”, for which, however, there is very little data in the public domain, in particular on use on the battlefield.
At this point, it is worth recalling that in 2024, the Russian Federation reformed the “1st Army Corps” (TOT of Donetsk region) into the 51st Combined Arms Army, and the “2nd Army Corps” (TOT of Luhansk region) into the 3rd Combined Arms Army.

At the same time, the authors of Defence24 emphasize that there is also very little data on the formation of units with the status of “infantry” in the directly “regular” troops of the Russian Federation in the public domain. Here we can only cite mentions of the “mysterious” 67th Infantry Regiment as part of the 90th Tank Division, and also about:
- the 11th Infantry Battalion from the 144th Motorized Rifle Division and the 15th Infantry Battalion from the 3rd Motorized Rifle Division (20th Army, Moscow MD);
- 28th Combined Infantry Battalion from the 60th Separate Mechanized Brigade (5th Army of the Eastern MD);
- and the 29th Infantry Battalion from the 38th Separate Motorized Rifle Brigade (35th Army of the Eastern MD).
From News Hub, we emphasize that although the above data look extremely fragmentary, they provide some understanding, in particular, on how the ruscists used “manpower” illegally and forcibly mobilized in the temporarily occupied part of Donbas in the war against Ukraine.

